- URL:URL:https://<ndlayer-url>/locate
- Version Introduced:11.1
Description
When performing analysis using routing services, the inputs to an analysis rarely fall exactly on top of the edges or junctions of the network dataset the service is using. For example, you may be using a network dataset constructed from street centerlines to power your routing services, and the input points you want to analyze are the centroids of parcels in your city. These parcel centroids do not fall on top of the street centerlines; rather, they are offset some distance from the streets. To successfully perform a network analysis using your routing services, the routing services must identify the location on the network dataset where each analysis input lies. This network location, rather than the input's original location, is used in the analysis. Typically, the longitude and latitude of the inputs are passed in and the routing services compute the location on the network during the solve operation. With the locate service, you can compute the locations on the network before calling the solve operation.
Learn more about locating inputs
The locate service is performed on a network dataset layer resource. You can provide arguments to the locate service as query parameters defined in the parameters table below. The locate service can be used in scenarios such as the following:
- Reuse location fields during the solve operation—You have a set of regularly serviced customers. You can use the locate service to calculate location fields, and use the located inputs in the routing services. This helps to speed up routing services since the service doesn't need to locate inputs again and you can reuse the locations in multiple places.
Nota:
The settings and barriers you use to locate inputs should match the eventual analysis settings when you perform routing service; otherwise, the routing services may still relocate because the locations are not valid for a different travel mode or with barriers.
- Compute serviceability—Before you perform a routing request, you can call locate to determine serviceability. For example, the mode of travel may only allow service inputs that are 500 meters off the streets. You can perform a locate service with 500 meters as the search tolerance and determine which inputs cannot be serviced before you perform a more advanced routing service.
- Use DistanceToNetworkInMeters to calculate service time—You can gain information from the locate service response to fine-tune your routing service settings. For example, if you want to know how far each input is off network to perform delivery analysis, and it takes time to go from the parked vehicle location to the delivery location, you can use the DistanceToNetworkInMeters field for each record in the response. Once you know how far away the actual location is from the network, you can use a speed factor to calculate a service time for each input based on its distance off the network.
- Query fields from the underlying source features—The locate service also supports returning additional field values from the source features where the inputs are located. For example, you can set different curb approaches on the inputs depending on the type of road on which they're located. If the input is located on a major road, you can set it to right or left side of the vehicle, depending on the driving side of the country where it's located. If the input is located on a local road, either side of curb approach will work since a vehicle can cross a local road for a delivery.
Request parameters
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| inputLocations (Required) | One or more input locations. Syntax: |
| token (Required) | The identity of a user who has permissions to access the service. |
| f (Optional) | The response format. The default value is html. Values: html | json| pjson |
| travelMode (Optional) | The mode of transportation for the analysis. Value: JSON object |
| locateSettings (Optional) | Specify the settings that affect how inputs are located. Value: JSON object |
| barriers (Optional) | One or more points that act as temporary restrictions to prevent locating on streets that intersect with the point barriers. Syntax: |
| polylineBarriers (Optional) | One or more polyline barriers that act as temporary restrictions to prevent locating on streets that intersect with polyline barriers. Syntax: |
| polygonBarriers (Optional) | One or more polygon barriers that act as temporary restrictions to prevent locating on streets that intersect with polygon barriers. Syntax: |
| returnBarriers (Optional) | Specify whether barriers will be returned by the service. The default value is false. Values: true | false |
| returnPolylineBarriers (Optional) | Specify whether polyline barriers will be returned by the service. The default value is false. Values: true | false |
| returnPolygonBarriers (Optional) | Specify whether polygon barriers will be returned by the service. The default value is false. Values: true | false |
| outputSourceFieldNames (optional) | The fields from which the located source feature values will be retrieved. This parameter is specified as a comma-separated list of names. The values can be specified as in the example below: Nota:Estos valores son específicos de los servicios publicados con los datos de ArcGIS StreetMap Premium. Los valores serán diferentes si utiliza otros datos para el análisis. |
| outSR (Optional) | The spatial reference of the output geometries. |
Required parameters
inputLocations
Specify one or more locations to locate.
You can use a simple comma- and semicolon-based syntax if you are passing the input locations using their longitude and latitude values in the WGS84 coordinate system and don't need to pass additional fields for each location.
Simple syntax for incidentsinputLocations=x1,y1; x2, y2; ...; xn, yn
Example using simple syntaxinputLocations=-117.1957,34.0564; -117.184,34.0546
Attributes for inputLocations
You can specify attributes for each inputLocations using the FeatureSet object. The attributes listed below are predefined for inputLocations. If these attributes are specified, it may impact the location. Custom attributes that you specify for the inputLocations, will be included in the outputLocations parameter in the response.
- ObjectID
The object ID of the input. ObjectID is a unique identifier for each input. If the ObjectID is not specified, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output.
- SourceID
El identificador numérico de la clase de entidad de origen del dataset de red donde se ubica el punto de entrada.
- SourceOID
El ObjectID de la entidad del origen donde se ubica el punto de entrada.
- PosAlong
La posición a lo largo de la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea de origen. Este valor se almacena como ratio. Este campo es nulo si la ubicación de red hace referencia a un cruce.
- SideOfEdge
El lado del eje respecto a la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea. Este campo se limita a un dominio de dos valores: lado derecho (1) y lado izquierdo (2).
Nota:
SourceID, SourceOID, PosAlong, and SideOfEdge are location fields. If these fields are included in the input, and if allowAutoRelocate is set to false in the locateSettings parameter, the analysis will use the location fields as is, without relocating. Otherwise, the analysis will calculate the location of input based on the geometry of the input. These fields are not required or needed in most cases when using the locate service.
- CurbApproach
Specify the direction a vehicle can arrive at and depart from the input location.
Se debe especificar uno de los enteros enumerados en la columna Valor codificado de la siguiente tabla como un valor de este atributo. Los valores de la columna Configuración son los nombres descriptivos de los valores del atributo CurbApproach que puede haber visto al utilizar el software Extensión ArcGIS Network Analyst.
Setting Coded value Description Cualquier lado del vehículo
0
The vehicle can approach and depart the input location in either direction, so a U-turn is allowed at the input location. This is the default value. This setting can be chosen if it is possible and desirable for a vehicle to turn around at the input location. This decision may depend on the width of the road and the amount of traffic or whether the input location has a parking lot where vehicles can pull in and turn around.
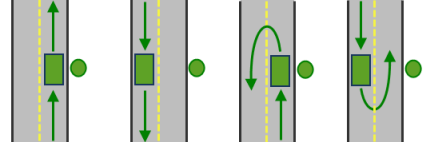
All arrival and departure combinations are allowed with the Either side of vehicle curb approach setting. Lado derecho del vehículo
1
When the vehicle approaches and departs the input location, the input location must be on the right side of the vehicle. A U-turn is prohibited. This is typically used for vehicles such as buses that must arrive with the bus stop on the right side.
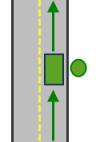
The allowed arrival and departure combination for the Right side of vehicle curb approach setting is shown. Lado izquierdo del vehículo
2
When the vehicle approaches and departs the input location, the input location must be on the left side of the vehicle. A U-turn is prohibited. This is typically used for vehicles such as buses that must arrive with the bus stop on the left side.
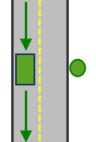
The allowed arrival and departure combination for the Left side of vehicle curb approach setting is shown. Sin cambio de sentido
3
When the vehicle approaches the input location, the input location can be on either side of the vehicle; however, when it departs, the vehicle must continue in the same direction it arrived. A U-turn is prohibited.
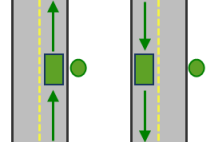
The allowed arrival and departure combinations for the No U-Turn curb approach setting is shown. The CurbApproach attribute is designed to work with both types of national driving standards: right-hand traffic (United States) and left-hand traffic (United Kingdom). First, consider a location on the left side of a vehicle. It is always on the left side regardless of whether the vehicle travels on the left or right half of the road. What may change with national driving standards is your decision to approach this location from one of two directions, that is, so it ends up on the right or left side of the vehicle. For example, if you want to arrive at a location and not have a lane of traffic between the vehicle and the location, choose 1 (Right side of vehicle) in the United States and 2 (Left side of vehicle) in the United Kingdom.

With right-hand traffic, the curb approach that leaves the vehicle closest to the input location is Right side of vehicle. 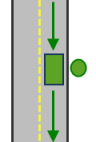
With left-hand traffic, the curb approach that leaves the vehicle closest to the input location is Left side of vehicle. - Bearing
La dirección en la que está avanzando un punto. Las unidades son grados y se miden en sentido horario desde el norte verdadero. Este campo se utiliza junto con el campo BearingTol.
Los datos de rumbo normalmente se envían de forma automática desde un dispositivo móvil dotado de un receptor GPS. Intente incluir datos de rumbo si está cargando una ubicación de entrada que se mueve, como un peatón o un vehículo.
Utilizar este campo tiende a evitar agregar ubicaciones a los ejes equivocados, que puede ocurrir cuando un vehículo está cerca de una intersección o un paso elevado, por ejemplo. El rumbo también ayuda a la herramienta a determinar en qué lado de la calle está el punto.
- BearingTol
El valor de tolerancia de rumbo crea un rango de valores de rumbo aceptable al ubicar los puntos en movimiento en un eje con el campo Bearing. Si el valor del campo Bearing está dentro del rango de valores aceptables que se generan a partir de la tolerancia de rumbo en un eje, el punto se puede agregar como una ubicación de red ahí; de lo contrario, se evalúa el punto más cercano sobre el próximo eje más cercano.
Las unidades se expresan en grados y el valor predeterminado es 30. Los valores deben ser mayores que 0 y menores que 180. Un valor de 30 significa que, cuando Network Analyst intenta agregar una ubicación de red en un eje, se genera un rango de valores de rumbo aceptable 15 grados hacia cada lado del eje (izquierda y derecha) y en ambas direcciones digitalizadas del eje.
- BuildTime
The build time stamp of the network dataset when the locations were last located. This is used when locating to know whether there is a need to relocate.
Example for inputLocations
Specify inputLocations geometries and attributes using a feature set object. This example shows how to specify the ObjectID, Name, and Tag attributes for each input location. (Name and Tag are examples of custom fields that contain information you may want to use in further analysis.)
{
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPoint",
"spatialReference": {
"wkid": 4326,
"latestWkid": 4326
},
"fields": [{
"name": "OBJECTID",
"type": "esriFieldTypeOID",
"alias": "OBJECTID"
},
{
"name": "Name",
"type": "esriFieldTypeString",
"alias": "Name",
"length": 500
},
{
"name": "Tag",
"type": "esriFieldTypeString",
"alias": "Tag",
"length": 1000
}
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"ObjectID": 1,
"Name": "Stop1",
"TAG": "TAG-001"
},
"geometry": {
"x": -122.4079,
"y": 37.78356
}
},
{
"attributes": {
"ObjectID": 2,
"Name": "Stop2",
"TAG": "TAG-002"
},
"geometry": {
"x": -122.404,
"y": 37.782
}
}
]
}token
Utilice este parámetro para especificar un token que proporcione la identidad de un usuario que tenga permisos para acceder al servicio. La página de seguridad y autenticación ofrece más información sobre cómo se puede obtener un token de acceso.
token=<yourToken>
Optional parameters
f
Utilice este parámetro para especificar el formato de respuesta. El parámetro puede tener html, json o pjson como argumentos, por ejemplo, f=json. El valor pjson se utiliza para imprimir la respuesta JSON en un formato embellecido.
travelMode
Seleccione el modo de transporte para el análisis.
The selected travel mode may affect locating input locations, because some streets that are restricted for vehicles may not be restricted for pedestrians. When locating the input locations, the restrictions on the travel mode are taken into consideration so the service doesn't locate on restricted elements.
Los modos de viaje se administran en ArcGIS Enterprise y el administrador de su organización puede configurarlos para reflejar mejor los flujos de trabajo de la organización.
Para obtener más información sobre los modos de viaje, consulte Configurar modos de viaje.
El valor del parámetro travelMode es el objeto JSON que contiene la configuración de un modo de viaje compatible con su organización. Para obtener los modos de viaje admitidos, ejecute el servicio retrieveTravelModes.
Puede hacer una solicitud para recuperar modos de viaje utilizando el siguiente formulario:
https://machine.domain.com/webadaptor/rest/services/Routing/NetworkAnalysis/NAServer/Routing_ND/retrieveTravelModes?f=json&token=<yourToken>Nota:
Consulte Implementar inicio de sesión de aplicación para ArcGIS Online y Adquirir tokens de ArcGIS para ArcGIS Enterprise para obtener información sobre cómo generar uno.
El servicio retrieveTravelModes devuelve la respuesta siguiente.
Nota:
Dado que la respuesta es muy detallada, los elementos de la respuesta se abrevian para mayor claridad.
{
"currentVersion": 11.1,
"defaultTravelMode": "FEgifRtFndKNcJMJ",
"supportedTravelModes": [
{
"attributeParameterValues": [
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Private Roads",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_MEDIUM"
},
{
"attributeName": "Walking",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Preferred for Pedestrians",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PREFER_LOW"
},
{
"attributeName": "WalkTime",
"parameterName": "Walking Speed (km/h)",
"value": 5
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Roads Unsuitable for Pedestrians",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_HIGH"
}
],
"description": "Follows paths and roads that allow pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel time. The walking speed is set to 5 kilometers per hour.",
"distanceAttributeName": "Kilometers",
"id": "caFAgoThrvUpkFBW",
"impedanceAttributeName": "WalkTime",
"name": "Walking Time",
"restrictionAttributeNames": [
"Avoid Private Roads",
"Avoid Roads Unsuitable for Pedestrians",
"Preferred for Pedestrians",
"Walking"
],
"simplificationTolerance": 2,
"simplificationToleranceUnits": "esriMeters",
"timeAttributeName": "WalkTime",
"type": "WALK",
"useHierarchy": false,
"uturnAtJunctions": "esriNFSBAllowBacktrack"
},
{
"attributeParameterValues": [
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Private Roads",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_MEDIUM"
},
{
"attributeName": "Walking",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Preferred for Pedestrians",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PREFER_LOW"
},
{
"attributeName": "WalkTime",
"parameterName": "Walking Speed (km/h)",
"value": 5
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Roads Unsuitable for Pedestrians",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_HIGH"
}
],
"description": "Follows paths and roads that allow pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel distance.",
"distanceAttributeName": "Kilometers",
"id": "yFuMFwIYblqKEefX",
"impedanceAttributeName": "Kilometers",
"name": "Walking Distance",
"restrictionAttributeNames": [
"Avoid Private Roads",
"Avoid Roads Unsuitable for Pedestrians",
"Preferred for Pedestrians",
"Walking"
],
"simplificationTolerance": 2,
"simplificationToleranceUnits": "esriMeters",
"timeAttributeName": "WalkTime",
"type": "WALK",
"useHierarchy": false,
"uturnAtJunctions": "esriNFSBAllowBacktrack"
},
{
"attributeParameterValues": [
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Private Roads",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_MEDIUM"
},
{
"attributeName": "Driving an Automobile",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Through Traffic Prohibited",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_HIGH"
},
{
"attributeName": "TravelTime",
"parameterName": "Vehicle Maximum Speed (km/h)",
"value": 0
},
{
"attributeName": "Roads Under Construction Prohibited",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Gates",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_MEDIUM"
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Express Lanes",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Carpool Roads",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
}
],
"description": "Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel time. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars, but does not discourage travel on unpaved roads. When you specify a start time, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where it is available.",
"distanceAttributeName": "Kilometers",
"id": "NmNhNDUwZmE1YTlj",
"impedanceAttributeName": "TravelTime",
"name": "Rural Driving Time",
"restrictionAttributeNames": [
"Avoid Carpool Roads",
"Avoid Express Lanes",
"Avoid Gates",
"Avoid Private Roads",
"Driving an Automobile",
"Roads Under Construction Prohibited",
"Through Traffic Prohibited"
],
"simplificationTolerance": 10,
"simplificationToleranceUnits": "esriMeters",
"timeAttributeName": "TravelTime",
"type": "AUTOMOBILE",
"useHierarchy": true,
"uturnAtJunctions": "esriNFSBAtDeadEndsAndIntersections"
},
{
"attributeParameterValues": [
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Private Roads",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_MEDIUM"
},
{
"attributeName": "Driving an Automobile",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Through Traffic Prohibited",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_HIGH"
},
{
"attributeName": "TravelTime",
"parameterName": "Vehicle Maximum Speed (km/h)",
"value": 0
},
{
"attributeName": "Roads Under Construction Prohibited",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Gates",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "AVOID_MEDIUM"
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Express Lanes",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
},
{
"attributeName": "Avoid Carpool Roads",
"parameterName": "Restriction Usage",
"value": "PROHIBITED"
}
],
"description": "Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel distance. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars, but does not discourage travel on unpaved roads.",
"distanceAttributeName": "Kilometers",
"id": "Yzk3NjI1NTU5NjVj",
"impedanceAttributeName": "Kilometers",
"name": "Rural Driving Distance",
"restrictionAttributeNames": [
"Avoid Carpool Roads",
"Avoid Express Lanes",
"Avoid Gates",
"Avoid Private Roads",
"Driving an Automobile",
"Roads Under Construction Prohibited",
"Through Traffic Prohibited"
],
"simplificationTolerance": 10,
"simplificationToleranceUnits": "esriMeters",
"timeAttributeName": "TravelTime",
"type": "AUTOMOBILE",
"useHierarchy": true,
"uturnAtJunctions": "esriNFSBAtDeadEndsAndIntersections"
},
...
],
}Desde el JSON anterior, para pasar Walking Time como modo de viaje, utilice el siguiente JSON como valor para el parámetro travelMode:
travelMode={"attributeParameterValues": [{"parameterName": "Restriction Usage","attributeName": "Walking","value": "PROHIBITED"},{"parameterName": "Restriction Usage","attributeName": "Preferred for Pedestrians","value": "PREFER_LOW"},{"parameterName": "Walking Speed (km/h)","attributeName": "WalkTime","value": 5}],"description": "Follows paths and roads that allow pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel time. The walking speed is set to 5 kilometers per hour.","impedanceAttributeName": "WalkTime","simplificationToleranceUnits": "esriMeters","uturnAtJunctions": "esriNFSBAllowBacktrack","restrictionAttributeNames": ["Preferred for Pedestrians","Walking"],"useHierarchy": false,"simplificationTolerance": 2,"timeAttributeName": "WalkTime","distanceAttributeName": "Miles","type": "WALK","id": "caFAgoThrvUpkFBW","name": "Walking Time"}locateSettings
Use este parámetro para especificar configuraciones que afecten a cómo se ubican las entradas, como la máxima distancia de búsqueda que se usa al localizar las entradas en la red, o las fuentes de red que se usan para localizar. Para restringir la ubicación en una parte del origen, puede especificar una cláusula WHERE para un origen.
El valor de parámetro se especifica como un objeto JSON. El objeto JSON le permite especificar un JSON de localizador para todas las entidades de entrada en el análisis o puede especificar una excepción para una entrada concreta. La excepción le permite tener diferentes ajustes para cada entrada de análisis. Por ejemplo, es posible no permitir que las paradas se ubiquen en las rampas de autopista y permitir que las barreras de punto se ubiquen en las rampas de autopista. Al especificar el JSON locateSettings, deberá proporcionar todas las propiedades, incluidas tolerance, toleranceUnits, sources y allowAutoRelocate en el objeto JSON de localizador predeterminado. La cláusula where para cada fuente es opcional. Si necesita proporcionar un JSON de localizador diferente para una clase de entrada en particular, debe incluir la propiedad de invalidaciones para esa entrada. El nombre de propiedad debe coincidir con el nombre del parámetro de entrada. El JSON del localizador de una entrada concreta no tiene que incluir todas las propiedades; solo tiene que incluir las propiedades que son distintas de las propiedades del JSON del localizador predeterminado.
Más información sobre la localización de entradas
Nota:
To obtain the default value for the parameter, see the network dataset layer resource.
The locator JSON object has the following properties:
- tolerance and toleranceUnits—Allows you to control the maximum
search distance when locating inputs. If no valid network
location is found within this distance, the input features will be
considered unlocated. A small search tolerance decreases the
likelihood of locating on the wrong street but increases the
likelihood of not finding any valid network location. The toleranceUnits parameter value should be specified as one of the following
values:
- esriFeet
- esriKilometers
- esriMeters
- esriMiles
- esriNauticalMiles
- esriYards
- sources—Allows you to control which network source can be used for
locating. For example, you can configure the analysis to locate
inputs on streets but not on sidewalks. The list of possible
sources on which to locate is specific to the network dataset this
service references. Only the sources that are present in the sources
array are used for locating. Optionally, you can specify a whereclause on each source you specified in the sources array to
further restrict locating on that source matching certain
characteristics using a SQL expression. For example, you can configure the analysis
to locate inputs only on street features matching certain road
classes, for example, to avoid highway ramps. Sources is specified
as an array of objects, each having the following
properties:
- name—The name of the network source feature class that can be used for locating inputs.
- where—An SQL expression on the network source feature class.
- allowAutoRelocate—Allows you to control whether inputs with existing network location fields can be automatically relocated to ensure valid, routable location fields for the analysis. If the value is true, points located on restricted network elements and points affected by barriers will be relocated to the closest routable location. If the value is false, network location fields will be used as is even if the points are unreachable. Even if the value is false, inputs with no location fields or incomplete location fields will be located.
Syntax for locateSettings
Syntax for specifying locateSettings using JSON structure.
Nota:
Polyline barriers and polygon barriers doesn't support the tolerance and toleranceUnits properties.
{
"default": {
"tolerance": <value>,
"toleranceUnits": "<unit>",
"allowAutoRelocate": true | false,
"sources": [{
"name": "<sourceName>",
"where": "<whereClause>"
}]
},
"overrides": {
"inputLocations": {
"tolerance": <value>,
"toleranceUnits": "<unit>",
"allowAutoRelocate": true | false,
"sources": [{
"name": "<sourceName>",
"where": "<whereClause>"
}]
},
"barriers": {
"tolerance": <value>,
"toleranceUnits": "<unit>",
"allowAutoRelocate": true | false,
"sources": [{
"name": "<sourceName>",
"where": "<whereClause>"
}]
},
"polylineBarriers": {
"allowAutoRelocate": true | false,
"sources": [{
"name": "<sourceName>",
"where": "<whereClause>"
}]
},
"polygonBarriers": {
"allowAutoRelocate": true | false,
"sources": [{
"name": "<sourceName>",
"where": "<whereClause>"
}]
}
}
}Examples for locateSettings
Ejemplo 1: especificar la configuración predeterminada de localización mediante una estructura JSON
This example shows how to specify locate settings so inputs are only located within 500 meters of the specified location. A small search tolerance like this may be valuable if you are locating using a walking travel mode and don't want inputs to be located farther than 500 meters from the original point location.{
"default": {
"tolerance": 500,
"toleranceUnits": "esriMeters",
"allowAutoRelocate": true,
"sources": [{
"name": "Routing_Streets"
}]
}
}
Ejemplo 2: especificar la configuración de localización predeterminada y las excepciones de la configuración de localización de algunas entradas mediante una estructura JSON
This example shows how to specify locate settings to prevent input locations from locating on highway ramps. The
default locate settings allow locating on the Routing_Streets
source. For input locations, the overrides option is used
to specify a where clause for the Routing_Streets source to prevent
locating on highway ramps (a ROAD_CLASS field value of 3). With
this locateSettings JSON, input locations cannot locate on
highway ramps, but barriers can because they use the default locate
settings, which do not include a where clause.
{
"default": {
"tolerance": 20,
"toleranceUnits": "esriKilometers",
"allowAutoRelocate": true,
"sources": [{
"name": "Routing_Streets"
}]
},
"overrides": {
"inputLocations": {
"sources": [{
"name": "Routing_Streets",
"where": "ROAD_CLASS <> 3"
}]
}
}
}
barriers
Use this parameter to specify one or more points that will act as temporary restrictions on the underlying streets. For example, a point barrier can be used to represent a fallen tree along a street.
Puede utilizar una sintaxis simple basada en comas y en punto y coma si pasa las ubicaciones de barrera de punto con sus valores de longitud y latitud en el sistema de coordenadas WGS84 y no necesita pasar campos adicionales para cada ubicación.
Sintaxis simple para barrerasbarriers=x1,y1; x2, y2; ...; xn, yn
Ejemplo con la sintaxis simplebarriers=-117.1957,34.0564; -117.184,34.0546
Attributes for barriers
You can specify attributes for each barrier using the FeatureSet object. The attributes listed below are predefined on the barriers. Locating the barrier may be impacted if these attribute values are specified.
ObjectID
The object ID of the barrier. The ObjectID is a unique identifier for each barrier. If no ObjectID is specified, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output.
SourceID
El identificador numérico de la clase de entidad de origen del dataset de red donde se ubica el punto de entrada.
SourceOID
El ObjectID de la entidad del origen donde se ubica el punto de entrada.
PosAlong
La posición a lo largo de la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea de origen. Este valor se almacena como ratio. Este campo es nulo si la ubicación de red hace referencia a un cruce.
SideOfEdge
El lado del eje respecto a la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea. Este campo se limita a un dominio de dos valores: lado derecho (1) y lado izquierdo (2).
Nota:
SourceID, SourceOID, PosAlong, and SideOfEdge are location fields. If these fields are present on the barrier, and if allowAutoRelocate is set to false in the locateSettings parameter, the analysis will use the location fields as is without relocating. Otherwise, the analysis will calculate the location of the barrier based on the geometry of the barrier. These fields are not required or needed in most locate service cases.
Example for barriers
Specify barrier geometries and attributes using a FeatureSet object.
This example shows how to specify barriers using ObjectID:
{
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPoint",
"spatialReference": {
"wkid": 4326,
"latestWkid": 4326
},
"fields": [{
"name": "ObjectID",
"type": "esriFieldTypeOID",
"alias": "ObjectID"
}
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"ObjectID": 1
},
"geometry": {
"x": -122.053461,
"y": 37.541479
}
}]
}polylineBarriers
Use this parameter to specify one or more lines that prohibit travel anywhere the lines intersect the streets. For example, a parade or protest that blocks traffic across several street segments can be modeled with a polyline barrier.
Attributes for polylineBarriers
You can specify attributes for each polyline barrier using the FeatureSet object. The following attributes are predefined on the polyline barriers. Locating the barrier may be impacted if these attributes are specified.
ObjectID
The object ID of the line barrier. The ObjectID is a unique identifier for the line barrier. If no ObjectID is specified, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output.
Locations
The locations range BLOB field representing the location of the polyline barrier on the network
Nota:
If the locations field is present on the polylineBarriers, and if allowAutoRelocate is set to false in the locateSettings parameter, the analysis will use the location fields as is without relocating. Otherwise, the analysis will calculate the location of the polyline barrier based on the geometry of the line barrier. This field is not required or needed in most locate service cases.
Example for polylineBarriers
Specify polylineBarriersgeometries and attributes using a feature set object.
This example shows how to specify polyline barriers using ObjectID.
{
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPolyline",
"spatialReference": {
"wkid": 4326,
"latestWkid": 4326
},
"fields": [{
"name": "ObjectID",
"type": "esriFieldTypeOID",
"alias": "ObjectID"
}
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"ObjectID": 1
},
"geometry": {
"paths": [
[
[-117.15881790299994, 32.721517814000038],
[-117.15873274499995, 32.71621669600006]
]
]
}
}]
}polygonBarriers
Use this parameter to specify polygons that restrict travel on the streets intersected by the polygons.
Attributes for polygonBarriers
You can specify attributes for each polygon barrier using the FeatureSet object. The attributes listed below are predefined on the polygon barriers. Locating the barrier may be impacted if these attributes are specified.
ObjectID
The object ID of the polygon barrier. The ObjectID is a unique identifier for the polygon barrier. If no ObjectID is specified, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output.
Locations
The locations range BLOB field representing the location of the polygon barrier on the network.
Nota:
If the locations field is present on the polylgonBarriers, and if allowAutoRelocate is set to false in the locateSettings parameter, the analysis will use the location fields as is without relocating. Otherwise, the analysis will calculate the location of the polygon barrier based on the geometry of the polygon barrier. This field is not required or needed in most locate service cases.
Example for polygonBarriers
Specify polygonBarriersgeometries and attributes using a feature set object.
This example shows how to specify polygon barriers using ObjectID.
{
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPolygon",
"spatialReference": {
"wkid": 4326,
"latestWkid": 4326
},
"fields": [{
"name": "ObjectID",
"type": "esriFieldTypeOID",
"alias": "ObjectID"
}
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"ObjectID": 1
},
"geometry": {
"rings": [
[
[-117.16058494299995, 32.715982512000039],
[-117.15681667899997, 32.715939932000026],
[-117.15690183699996, 32.711809745000039],
[-117.16064881099999, 32.71180974400005],
[-117.16058494299995, 32.715982512000039]
]
]
}
}]
}returnBarriers
Specify whether barriers will be returned by the service.
- true—The input point barriers are returned as part of the barriers property in the JSON response.
- false—Point barriers are not returned. This is the default.
For this parameter to take effect, you must also specify a value for the barriers parameter.
You can set the returnBarriers parameter to true to see where the barriers were located on the street network or, if they weren't located, understand what the problem was by checking the Status property in the JSON response.
returnPolylineBarriers
Specify whether polyline barriers will be returned by the service.
- true—The input polyline barriers are returned as part of the polylineBarriers property in the JSON response.
- false—Polyline barriers are not returned. This is the default.
For this parameter to take effect, you must also specify a value for the polylineBarriers parameter.
returnPolygonBarriers
Specify whether polygon barriers will be returned by the service.
- true—The input polygon barriers are returned as part of the polygonBarriers property in the JSON response.
- false—Polygon barriers are not returned. This is the default.
For this parameter to take effect, you must also specify a value for the polygonBarriers parameter.
outputSourceFieldNames
Use this parameter to specify the fields from which the located source feature values will be retrieved. The parameter is specified as a comma-separated list of names.
For example, you may want to know the road class for the feature where the inputs are located so you know whether the inputs are located on a local road, major road, or highway. This information can be helpful to set the curb approach for the input when you use other routing services to solve, so your drivers don't cross a major road or highway for a delivery. Another example is you know the street names where the inputs are supposed to locate, and you want to know the street name where the inputs located during the locate process so you can validate they locate on the correct feature. In this case, you can set outputSourceFieldNames to the fields you are interested in. For example, if you want to return both road class and street name, you can specify outputSourceFieldNames as "ROAD_CLASS, FULL_STREET_NAME" (ROAD_CLASS, FULL_STREET_NAME for the fields on the street source feature of the ArcGIS StreetMap Premium network dataset. (The fields may be different if you use other data for the service). You can find the field names for each source feature by querying network dataset layer resource.
If the feature where the input is located doesn't have the field you specified, it will not be included in the output. If you have multiple inputs that locate on different feature classes, some fields might exist on one feature but not the other. In those cases, the field will be included in the output, but the value may be empty.
outSR
Utilice este parámetro para especificar la referencia espacial de las geometrías, como entidades de líneas o puntos, que devuelve un servicio.
El valor del parámetro se puede especificar como un Id. conocido (WKID) para la referencia espacial. Consulte Utilizar referencias espaciales para buscar valores de WKID.
Muchos de los mapas base proporcionados por ArcGIS Online están en la referencia espacial Web Mercator (WKID 102100). Al especificar outSR=102100 se devuelven las geometrías de la referencia espacial Web Mercator, que se pueden dibujar sobre los mapas base.
Output parameters
Upon successful operation, the service returns the located inputs and barriers if requested. The status field on the outputs indicates whether each feature is located. The service won't fail if the inputs are not located, so you need to inspect the status field to know which features are located and which features are not. The fields for each output are described below. Custom fields defined on inputs are included in the output but are not included in the table below.
outputLocations
This provides access to the attributes of the locations located by the service. You can use the attributes from this parameter, such as the Status field, to determine whether a particular input was located.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
ObjectID | The value for this field will be the ObjectID of the associated input. If the ObjectID is not specified on the input, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output. |
SourceID | El identificador numérico de la clase de entidad de origen del dataset de red donde se ubica el punto de entrada. |
SourceOID | El ObjectID de la entidad del origen donde se ubica el punto de entrada. |
PosAlong | La posición a lo largo de la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea de origen. Este valor se almacena como ratio. Este campo es nulo si la ubicación de red hace referencia a un cruce. |
SideOfEdge | El lado del eje respecto a la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea. Este campo se limita a un dominio de dos valores: lado derecho (1) y lado izquierdo (2). |
CurbApproach |
The direction a vehicle can arrive at and depart from the stop. The values for this field are copied from the CurbApproach field on the input stops. |
Status | Specifies the status of the point with respect to its location on the network and the outcome of the analysis. The possible values are the following:
|
SnapX | La coordenada x de la posición en el dataset de red donde se ubica el punto, en el sistema de coordenadas del dataset de red. |
SnapY | La coordenada y de la posición en el dataset de red donde se ubica el punto, en el sistema de coordenadas del dataset de red. |
SnapZ | La coordenada z de la posición en el dataset de red donde se ubica el punto, en el sistema de coordenadas del dataset de red. El campo SnapZ es 0 si la red es bidimensional. |
DistanceToNetworkInMeters | La distancia en metros entre la ubicación geográfica del punto y la posición en la que se ubicaba en la red. |
BuildTime | The build timestamp of the network dataset used by the locating service. |
barriers
This provides access to attributes of the barriers located by the service.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
ObjectID | The value for this field will be the ObjectID of the associated input. If the ObjectID is not specified on the input, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output. |
SourceID | El identificador numérico de la clase de entidad de origen del dataset de red donde se ubica el punto de entrada. |
SourceOID | El ObjectID de la entidad del origen donde se ubica el punto de entrada. |
PosAlong | La posición a lo largo de la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea de origen. Este valor se almacena como ratio. Este campo es nulo si la ubicación de red hace referencia a un cruce. |
SideOfEdge | El lado del eje respecto a la dirección digitalizada de la entidad de línea. Este campo se limita a un dominio de dos valores: lado derecho (1) y lado izquierdo (2). |
CurbApproach |
The direction a vehicle can arrive at and depart from the stop. The values for this field are copied from the CurbApproach field on the input stops. |
Status | Specifies the status of the point with respect to its location on the network and the outcome of the analysis. The possible values are the following:
|
SnapX | La coordenada x de la posición en el dataset de red donde se ubica el punto, en el sistema de coordenadas del dataset de red. |
SnapY | La coordenada y de la posición en el dataset de red donde se ubica el punto, en el sistema de coordenadas del dataset de red. |
SnapZ | La coordenada z de la posición en el dataset de red donde se ubica el punto, en el sistema de coordenadas del dataset de red. El campo SnapZ es 0 si la red es bidimensional. |
DistanceToNetworkInMeters | La distancia en metros entre la ubicación geográfica del punto y la posición en la que se ubicaba en la red. |
BuildTime | The build timestamp of the network dataset used by the locating service. |
polylineBarriers
This provides access to attributes of the polyline barriers located by the service.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
ObjectID | The value for this field will be the ObjectID of the associated input. If the ObjectID is not specified on the input, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output. |
Locations | The location ranges of polyline barriers as base64. |
BarrierType | Specify if the barrier restricts travel completely or scales time or distance when it is crossed. The value for this attribute is specified as one of the following integers (use the numeric code, not the name in parentheses):
|
polygonBarriers
This provides access to attributes of the polygon barriers located by the service.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
ObjectID | The value for this field will be the ObjectID of the associated input. If the ObjectID is not specified on the input, a unique ID is automatically generated in the output. |
Locations | The location ranges of polygon barriers as base64. |
BarrierType | Specify if the barrier restricts travel completely or scales time or distance when it is crossed. The value for this attribute is specified as one of the following integers (use the numeric code, not the name in parentheses):
|
JSON Response syntax
The JSON response from the locate service is based on the syntax below. The actual properties returned in the response depend on the request parameters. For example, the barriers property is returned only if returnBarriers is set to true. If a request fails, the JSON response only contains the error property. The examples in the subsequent section illustrate the response returned with specific request parameters.
JSON Response syntax for a successful request
{
"requestID": "<requestID>",
"outputLocations": {
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPoint",
"spatialReference": {<spatialReference>},
"fields": [{
"name": "<fieldName>",
"type": "<fieldType>",
"alias": "<fieldAlias>"
},
...
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"<fieldName>": <fieldValue>,
...
},
"geometry": {<point>}
},
...
]
},
"barriers": {
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPoint",
"spatialReference": {<spatialReference>},
"fields": [{
"name": "<fieldName>",
"type": "<fieldType>",
"alias": "<fieldAlias>"
},
...
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"<fieldName>": <fieldValue>,
...
},
"geometry": {<point>}
},
...
]
},
"polylineBarriers": {
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPolyline",
"spatialReference": {<spatialReference>},
"fields": [{
"name": "<fieldName>",
"type": "<fieldType>",
"alias": "<fieldAlias>"
},
...
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"<fieldName>": <fieldValue>,
...
},
"geometry": {<polyline>}
},
...
]
},
"polygonBarriers": {
"displayFieldName": "",
"geometryType": "esriGeometryPolygon",
"spatialReference": {<spatialReference>},
"fields": [{
"name": "<fieldName>",
"type": "<fieldType>",
"alias": "<fieldAlias>"
},
...
],
"features": [{
"attributes": {
"<fieldName>": <fieldValue>,
...
},
"geometry": {<polygon>}
},
...
]
}
}JSON Response syntax for a failed request
{
"error": {
"code": <code>,
"message": "<message>",
"details": [
"<details>"
]
}
}